Infalling on to the black hole may drive materials crazy. How on earth can they keep their sanity while all bodies undergo extreme gravity? These days, most researchers who are simulating an accreting flow around a black hole choose the condition of the accretion disc between the “SANE” and “MAD”. Now you may think that the infalling materials would be CRAZIER in the “MAD” disc than the other. In fact, the component for dividing “SANE” and “MAD” is the strength of poloidal magnetic fields. “SANE” stands for Standard and Normal Evolution, and “MAD” stands for Magnetically Arrested Disc. Over the decades, the magnetic field structures around the central black hole…
Read More >>-
-
The curious case of FR0s: The relatively new class of radio galaxy
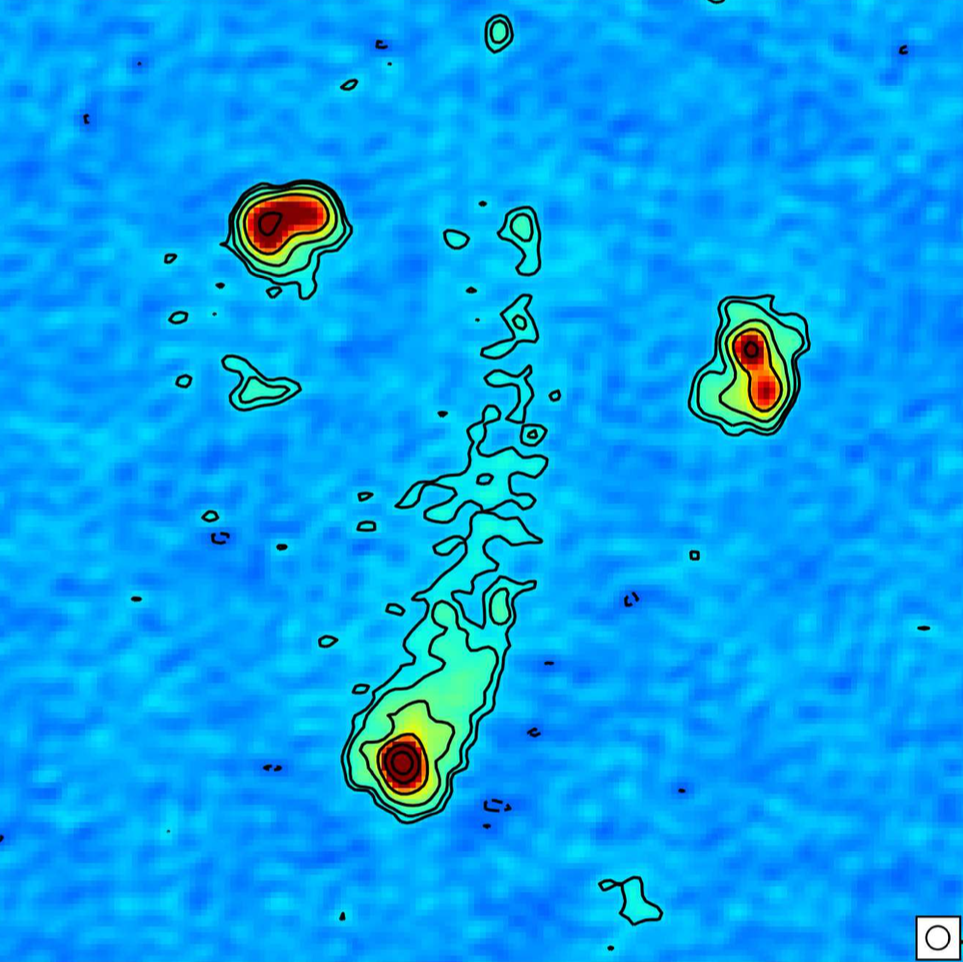
Radio galaxies are a class of active galactic nuclei that shine very brightly at radio frequencies but also radiate across the entire electromagnetic spectrum too. Powered by accretion of matter onto a central fast-spinning supermassive black hole, radio galaxies can display extended radio structures- jets. Jets emit radiation strongly at radio frequencies and can propagate hundreds of kiloparsecs (1 kiloparsec = 3.086 x 1016 km) or more beyond the central black hole that powers them. Jets travel with relativistic velocities, carrying large amounts of energy with them to regions well outside the confines of their host galaxy. Radio galaxies which display these jets can be classified based on their morphology…
Read More >> -
MasterChef Universe : Spaghetti(fication) with Black Holes (Part II)
This is second part in the series of posts about Spaghettification. In this part we go over the idea of how gravity squeezes objects. We will also briefly discuss how to make tidal forces stronger. Squeezing Now let’s rotate the rod so that it is oriented with both ends equally distant from the Earth, while the rod’s mid point is still located at a distance R from the Earth’s center. Unlike the case when the rod was vertical, here the Earth pulls at both these ends with an equal force directed towards the Earth’s center (white arrows in Figure 2). The force at the left end (point A) can be…
Read More >> -
MasterChef Universe : Spaghetti(fication) with Black Holes (Part I)
Can black holes make spaghetti? Like Obama, black holes would reply ‘Yes we can’! To top that off they can make spaghetti out of anything – using their ‘gravitational machinery’. In this three part series we will see how black holes employ gravity to do so! Before we go exploring black hole’s ‘spaghetti skills’, in part I, first let us look closer to home, at our very own Earth’s ‘spaghetti skills’ and its connection to the concept of tidal forces. Gravity and Tidal Force Let’s begin with the familiar. Earth produces a gravitational field by the virtue of its mass, and objects immersed in this field feel a gravitational force.…
Read More >> -
Can you Discriminate between Space and Time? (Part III)
In part II we saw that in a non-rotating black hole, the spatial and temporal coordinates are exchanged. Now we can take a step further, to consider the case of a rotating black hole. The line element in such spacetime has very complicated coefficients, but we don’t need the specific expressions here. So let’s just represent them in terms of the metric components: From the specific forms of those coefficients, we know that the dt2 and dϕ2 terms are always positive while the dtdϕ term is negative. What differs from the non-rotating case is, here the gtt and grr don’t switch signs at the same place, but at rH and…
Read More >> -
Can you Discriminate between Space and Time? (Part II)
In part I we showed that space and time coordinates lead to different types of interval, spacelike and timelike respectively. Hence if we are given a line element expression in terms of any coordinates, we can figure out which of the coordinates are spatial and temporal, by looking at the sign of their coefficients. The coordinate t is temporal not because of the variable used, but the timelike interval it creates. Now we may ask: if a coordinate is spatial or temporal, does it always keep this identity? The short answer is, no. More rigorously, it depends on the structure of spacetime. For flat spacetime as shown in the last…
Read More >> -
Can you Discriminate between Space and Time? (Part I)
What is the universe? All of space and time along with their contents. The unity of space and time is well-embodied in its Chinese term: Yu Zhou, where “Yu” means all of space and “Zhou” means all of time. However, what is space and what is time, and what is their difference? This is an ultimate puzzle for anyone exposed to special and general relativity. According to our daily sense, space and time are a set of concepts to quantify the events in the world. Every event occurs at a place in space and a moment in time. With such space and time coordinates, we can compare different events and…
Read More >> -
The best plot in astrophysics
In these last few years many fields in astrophysics have been advancing at an amazing rate. One of the fastest has been the study of the so-called “fast radio bursts” (or FRBs). As the name implies, FRBs are flashes of radio emission that happen extremely fast – down to a few milliseconds. This short duration makes them very challenging to detect, so the first FRB was only detected in 2007 at a facility called the Parkes Observatory. To complicate the picture, earlier on the Parkes Observatory detected another type of never seen before transient, called “perytons”. Early on it became clear that while it was possible for FRBs to be…
Read More >> -
Hadronic emission from the jets of X-ray binaries?
X-ray binaries with a Galactic black hole (BHXRBs) have recently been detected in GeV and TeV γ-rays. The radiative mechanism responsible for this emission is not yet fully understood and both leptonic and hadronic processes seem viable. In the former scenario, electrons are accelerated to high energies and dominate the non-thermal spectrum with synchrotron and inverse Compton scattering. In the latter case, protons are also accelerated as well and contribute (or even dominate) in the most energetic regime of the spectrum via neutral pion decay. In the past few years, I have been working on understanding these physical processes, focusing mostly on the hadronic ones. But allow me first to…
Read More >> -
Warps and twists around black holes
Twisted jets? Warped disks? It’s all possible in black holes! Hi all! Today I will talk a bit about our recent paper on the different types of disks you can have around black holes. As perhaps you would know, in 2019, the Event Horizon Telescope collaboration (EHTC) released the first-ever photos of the inner regions of the galaxy M87 (see link here). The EHTC studied an extensive suite of theoretical models of accreting black holes and tried to see which models looked similar to the observed images. These models simulate how the gas accretes onto a spinning or non-spinning black hole and then calculates how photons of light produced by…
Read More >>